|
© I contenuti di questa pagina (escluse le immagini di pubblico dominio) sono di proprietà esclusiva dell'autore Alberto Tucci. Ne è vietata la copia, la riproduzione e l'utilizzo anche parziale in ogni forma. |
| QUESTA SCHEDA È UNICA E ORIGINALE IN INTERNET - rev. 10-09-2025 |
ALBIZIA |
LEGGERE LA SCHEDA IN TUTTE LE SUE SEZIONI PER UNA CORRETTA INFORMAZIONE SULLE PRECAUZIONI D'USO
| COLORI OSSERVATI NEI FIORI |
| ________ BIANCO |
| ________ ROSA CHIARO |
| ________ ROSA GERANIO |
| ________ ROSA POLVEROSO |
| ________ ROSSO LAMPONE |
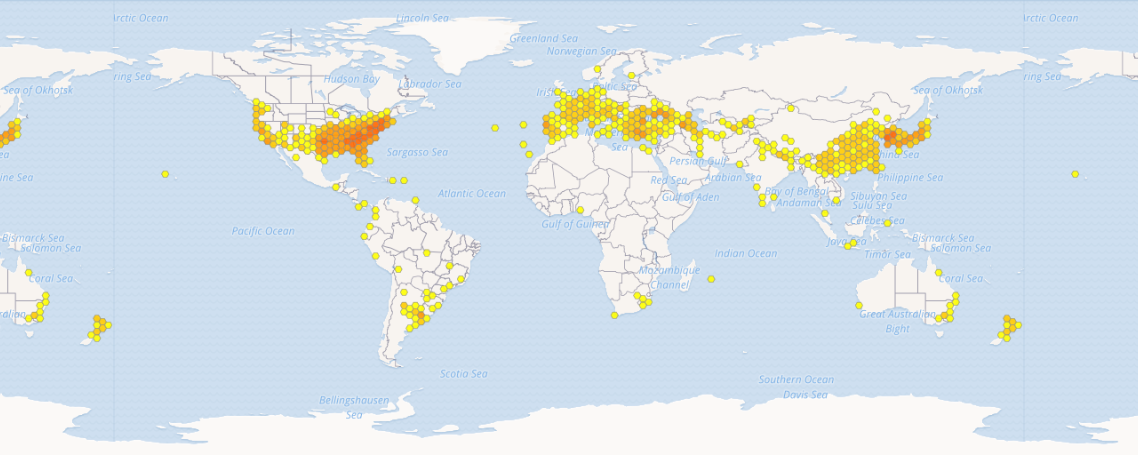
| DISTRIBUZIONE IN BASE ALLE OSSERVAZIONI UMANE |
 |
| *Note e Bibliografia relativa a proprietà e indicazioni |
| CONTROINDICAZIONI GRAVIDANZA, ALLATTAMENTO, IPERSENSIBILITÀ O ALLERGIA ACCERTATA VERSO ALBIZIA JULIBRISSIN O PIANTE DELLA FAMIGLIA FABACEAE, ETÀ PEDIATRICA, PAZIENTI CON DIAGNOSI O STORIA PREGRESSA DI PSICOSI O DISTURBI SCHIZOFRENICI, PAZIENTI IN TERAPIA CON FARMACI IPOTENSIVI PER IL RISCHIO DI EFFETTI ADDITIVI. |
| AVVERTENZE EVITARE L'USO CONCOMITANTE CON FARMACI SEDATIVI (BENZODIAZEPINE, BARBITURICI) PER RISCHIO DI ECCESSIVA SEDAZIONE, EVITARE L'USO CONCOMITANTE CON FARMACI ANTIDEPRESSIVI (SSRI, IMAO) PER RISCHIO DI SINDROME SEROTONINERGICA, EVITARE L'USO PRIMA DI GUIDARE O OPERARE MACCHINARI PER POSSIBILE SONNOLENZA, NON SUPERARE LE DOSI CONSIGLIATE A CAUSA DELLA PRESENZA DI ALCALOIDI INDOLICI IN TRACCE, SOSPENDERE L'ASSUNZIONE ALMENO DUE SETTIMANE PRIMA DI INTERVENTI CHIRURGICI PROGRAMMATI PER POTENZIALE EFFETTO IPOTENSIVO, CONSULTARE IL MEDICO IN CASO DI DIABETE PER POTENZIALE EFFETTO IPOGLICEMIZZANTE. |
| * Si tenga presente che talvolta la stessa erba indicata come sinergica o antagonista, potrebbe assumere entrambi i ruoli in funzione della dose utilizzata e/o della forma estrattiva o di trattamento come per es. nel Tè (verde o nero). Consultare sempre un fitoterapeuta per personalizzare le combinazioni in base al quadro clinico individuale. |
BIBLIOGRAFIA, WEBLIOGRAFIA E ARTICOLI SCIENTIFICI SUL WEB (Vedi anche i riferimenti nelle singole sezioni) |
.jpg)
Autore: Andrea Moro
.jpg)
Autore: Andrea Moro
.jpg)
Autore: Andrea Moro
 Altre Foto e Immagini di ALBIZIA
Altre Foto e Immagini di ALBIZIA